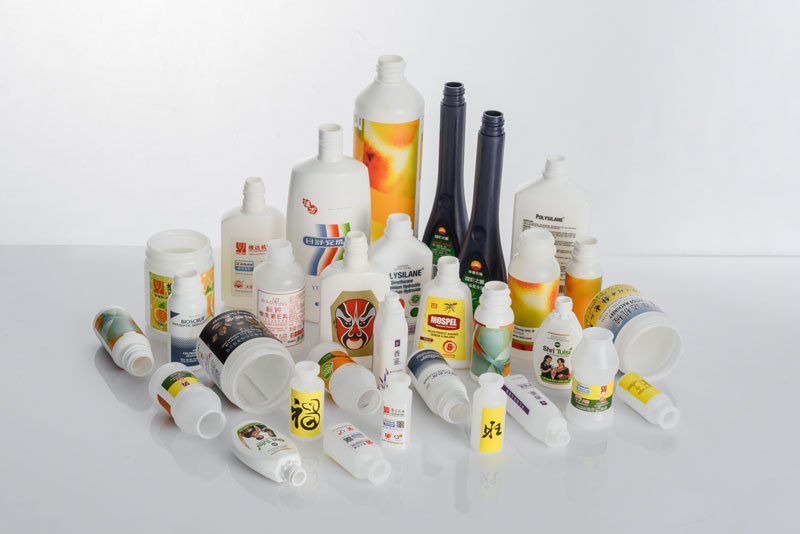
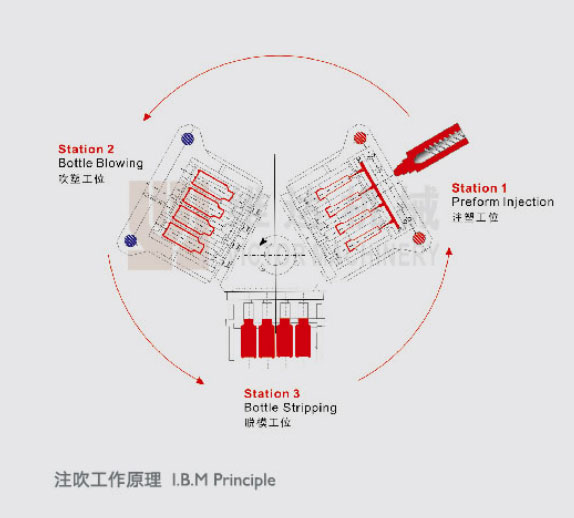
What Kind of Raw Material Pellets are Suitable for IBM Machines?
Finding the right raw material pellets for injection blow molding (IBM) machines can be tricky. But it’s essential to ensure smooth production and quality results.
The right raw material pellets for IBM machines make all the difference in achieving high-quality, efficient production. Here’s what you need to know to choose the best ones.

Injection blow molding machines play a key role in producing plastic products like bottles and jars. To ensure your production process runs smoothly, it’s critical to select the right type of raw material pellets. Let’s explore the factors involved in making the right choice.
What materials can be processed by injection-blow molding machines?
Not all materials are suitable for IBM machines, but the right ones can improve efficiency and product quality. Let’s take a look at what can be processed.
Injection blow molding machines are designed for thermoplastics. The most common materials processed by IBM include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and more.

IBM machines are designed to handle thermoplastic materials, which become moldable when heated and solidify as they cool. Below are the most common materials used in IBM:
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
- Common Uses: Detergent bottles, shampoo bottles
- Why It Works: HDPE is strong and durable. It has excellent resistance to stress cracking and is ideal for rigid containers.
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
- Common Uses: Squeeze bottles, flexible containers
- Why It Works: LDPE is flexible and transparent. It’s perfect for containers that need some pliability.
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene)
- Common Uses: Food containers, industrial applications
- Why It Works: LLDPE offers a balance of flexibility and toughness, making it versatile for a variety of applications.
PP (Polypropylene)
- Common Uses: Food containers, pharmaceutical bottles
- Why It Works: PP is heat-resistant and has good clarity. It’s often used in products exposed to higher temperatures.
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
- Common Uses: Toys, appliance shells
- Why It Works: HIPS is tough and easy to process, ideal for products requiring strength and durability.
PS/GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene)
- Common Uses: Disposable tableware, display trays
- Why It Works: PS is transparent and easy to mold, making it suitable for disposable products and packaging.
Each material is selected based on the product’s intended use and the machine's ability to handle it.
How to choose the right raw material pellets for IBM machines?
Choosing raw material pellets for IBM requires a careful evaluation of the materials’ characteristics. Several factors should guide your decision-making process.
The right choice of raw material pellets for IBM machines depends on product characteristics, performance, and cost considerations.

When selecting pellets for IBM, there are several critical factors to consider:
Product Usage and Characteristic Requirements
- Food-Grade Containers: If you’re manufacturing food containers, you must use pellets that meet food safety standards. This ensures the materials are safe for direct food contact.
- Durability and Flexibility: Some containers need to be rigid, while others need to be flexible. Select pellets based on the specific requirements of the product.
Forming Performance
- Flow and Fluidity: Different materials flow differently under heat. Some materials, like HDPE, flow more easily and fill the mold more completely, while others may need more time or heat to process effectively.
- Shrinkage Rate: Materials shrink at different rates as they cool. Understanding shrinkage is critical to ensure your final product matches the desired dimensions.
Cost Control
- Recycled vs. Virgin Materials: Virgin materials tend to offer better consistency, but recycled pellets can help lower production costs. However, recycled materials might impact the final product’s quality and appearance.
- Budget Considerations: It’s important to choose materials that fit within the production budget. Some materials are more expensive than others, and you may need to balance cost with quality.
These factors work together to ensure you select the right material that meets both product requirements and budget constraints.
What are the common materials used in injection blow molding?
Injection blow molding is used to create many products, and the choice of raw material affects both the process and the final result. Let’s dive deeper into the most commonly used materials.
The most common materials used in IBM include HDPE, LDPE, PP, and PS, each chosen for their specific properties that fit different types of products.

Here’s a closer look at the materials used in injection blow molding:
HDPE
- Common Uses: Detergent bottles, water bottles
- Advantages: HDPE is durable and resistant to cracking, making it the go-to material for products requiring strength and resistance to wear and tear.
LDPE
- Common Uses: Squeeze bottles, flexible containers
- Advantages: LDPE is more flexible than HDPE and offers good transparency, making it suitable for containers that need to be squeezed or bent.
LLDPE
- Common Uses: Packaging, industrial containers
- Advantages: Offers a blend of flexibility and toughness, making it ideal for both consumer and industrial products.
PP
- Common Uses: Food containers, pharmaceutical packaging
- Advantages: PP is heat-resistant and chemically resistant, making it perfect for food-related products or containers that need to withstand heat.
HIPS
- Common Uses: Toys, appliance parts
- Advantages: HIPS is strong and impact-resistant, making it ideal for products that need durability, such as toys and appliance shells.
PS
- Common Uses: Disposable tableware, packaging
- Advantages: PS is highly transparent and easy to mold, making it perfect for low-cost, high-clarity products.
Each of these materials brings something unique to the table, whether it's strength, flexibility, heat resistance, or transparency.
Are there any limitations on the types of materials that can be used?
While IBM machines are versatile, not all materials are a perfect fit. Let’s explore the limitations you need to consider when choosing materials.
IBM machines work best with thermoplastics, but some materials have limitations in terms of flow, cooling rates, and mold compatibility.

Even though IBM machines can handle various materials, some factors can limit their performance with certain materials:
Material Flow and Viscosity
- High Viscosity: Materials like PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) may not flow as easily in the mold due to their high viscosity. This can cause incomplete filling or uneven products.
- Inconsistent Cooling: Some materials shrink more than others, leading to potential issues with consistency and dimensional accuracy.
Mold Compatibility
- Detailed Molds: If your product requires an intricate mold design, you may need to select a material that can flow and fill the mold more easily. Materials that are too thick may not fill every detail.
- Thermal Sensitivity: Some biodegradable materials may deform or not hold up well under the high temperatures required in IBM. These materials might not be suitable for the injection blow molding process.
Being aware of these limitations will help you select materials that not only fit your product requirements but also optimize your production process.
Conclusion
Choosing the right raw material pellets for IBM machines ensures quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in production. By considering material properties and production needs, you can make the best choice for your specific application.